강좌 & 팁
안녕하세요~~ 호서대학교 석사(과정) 이우영입니다.
오늘도 활기차게 공부해봅시다!!!
저번 시간에 이어서 vm_area_struct 에 대해서 알아보겠습니다.
(mmu는 시간상 다음기회에 ㅎㅎ)
vm_area_struct
include/linux/mm_types.h 에 보면
116/* 117 * This struct defines a memory VMM memory area. There is one of these 118 * per VM-area/task. A VM area is any part of the process virtual memory 119 * space that has a special rule for the page-fault handlers (ie a shared 120 * library, the executable area etc). 121 */ 122struct vm_area_struct { 123 struct mm_struct * vm_mm; /* The address space we belong to. */ 124 unsigned long vm_start; /* Our start address within vm_mm. */ 125 unsigned long vm_end; /* The first byte after our end address 126 within vm_mm. */ 127 128 /* linked list of VM areas per task, sorted by address */ 129 struct vm_area_struct *vm_next; 130 131 pgprot_t vm_page_prot; /* Access permissions of this VMA. */ 132 unsigned long vm_flags; /* Flags, see mm.h. */ 133 134 struct rb_node vm_rb; 135 136 /* 137 * For areas with an address space and backing store, 138 * linkage into the address_space->i_mmap prio tree, or 139 * linkage to the list of like vmas hanging off its node, or 140 * linkage of vma in the address_space->i_mmap_nonlinear list. 141 */ 142 union { 143 struct { 144 struct list_head list; 145 void *parent; /* aligns with prio_tree_node parent */ 146 struct vm_area_struct *head; 147 } vm_set; 148 149 struct raw_prio_tree_node prio_tree_node; 150 } shared; 151 152 /* 153 * A file's MAP_PRIVATE vma can be in both i_mmap tree and anon_vma 154 * list, after a COW of one of the file pages. A MAP_SHARED vma 155 * can only be in the i_mmap tree. An anonymous MAP_PRIVATE, stack 156 * or brk vma (with NULL file) can only be in an anon_vma list. 157 */ 158 struct list_head anon_vma_node; /* Serialized by anon_vma->lock */ 159 struct anon_vma *anon_vma; /* Serialized by page_table_lock */ 160 161 /* Function pointers to deal with this struct. */ 162 struct vm_operations_struct * vm_ops; 163 164 /* Information about our backing store: */ 165 unsigned long vm_pgoff; /* Offset (within vm_file) in PAGE_SIZE 166 units, *not* PAGE_CACHE_SIZE */ 167 struct file * vm_file; /* File we map to (can be NULL). */ 168 void * vm_private_data; /* was vm_pte (shared mem) */ 169 unsigned long vm_truncate_count;/* truncate_count or restart_addr */ 170 171#ifndef CONFIG_MMU 172 struct vm_region *vm_region; /* NOMMU mapping region */ 173#endif 174#ifdef CONFIG_NUMA 175 struct mempolicy *vm_policy; /* NUMA policy for the VMA */ 176#endif 177}; 178 179struct core_thread { 180 struct task_struct *task; 181 struct core_thread *next; 182}; 183 184struct core_state { 185 atomic_t nr_threads; 186 struct core_thread dumper; 187 struct completion startup; 188};
그럼 이 구조체를 이용하여 메모리 영역을 출력 해보도록 하겠습니다.
10_VMA.c
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/sched.h>
int __init module_start( void )
{
struct task_struct *task;
struct mm_struct *mm;
struct vm_area_struct *mmap;
task = current;
mm = task->mm;
mmap = mm->mmap;
printk("task_id = %d\n",task->pid);
do
{
printk("vm_start = %8x ",mmap->vm_start);
printk("vm_end = %8x ",mmap->vm_end);
printk("vm_area = %8x\n",mmap->vm_end - mmap->vm_start);
}while(mmap = mmap->vm_next);
return -EBUSY;
}
void __exit module_end( void )
{
}
module_init(module_start);
module_exit(module_end);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
일단 출력 해 보면 다음과 같습니다.
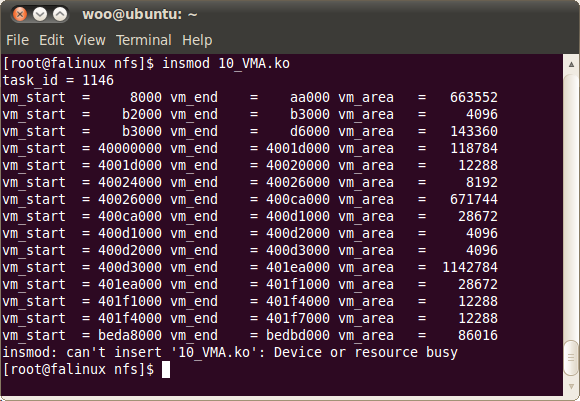
저런 식으로 출력한 이유는 다음 그림과 같습니다.
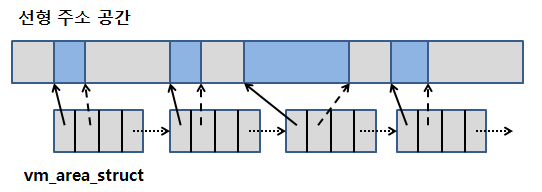 각 vm_area_struct는 메모리의 잡히는 공간을 가리키고 있습니다.
각 vm_area_struct는 메모리의 잡히는 공간을 가리키고 있습니다.
하나의 구조체로는 모두 표현하기도 힘들고 부부별로 할당하는 부분이 다르기 때문에
링크드 리스트를 이용하여 연결되어 있습니다.
ps 명령어를 첬을때 나오는 vsz는 kb단위 이기 때문에
printk("vm_area = %8x\n",(mmap->vm_end - mmap->vm_start) / 1024);
이런식으로 바꾸면 다음과 같습니다.
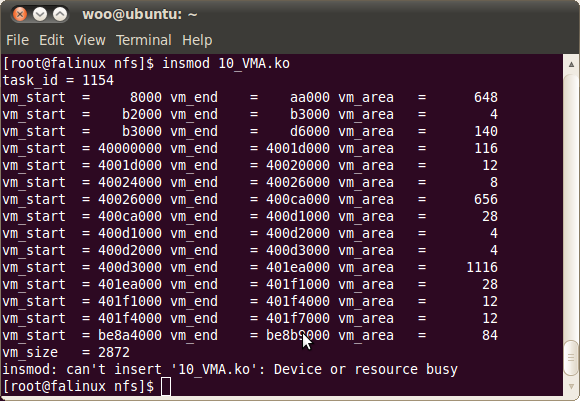
그리고 이 구조체들의 모든 영역을 더하면 2872kb 영역인것을 알 수 있습니다.
그럼 다시 모든 프로세스의 영역을 알아 볼까요?
11_all_task_VMA.c
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/sched.h>
int __init module_start( void )
{
struct task_struct *task;
struct mm_struct *mm;
struct vm_area_struct *mmap;
u32 size;
for_each_process(task)
{
size = 0;
printk("task_id = %4d ",task->pid);
if(mm = task->mm)
{
do
{
size = size + ((mmap->vm_end - mmap->vm_start) / 1024);
}while(mmap = mmap->vm_next);
printk("vm_size = %u ",size); }
else
printk("kernel task\n");
}
return -EBUSY;
}
void __exit module_end( void )
{
}
module_init(module_start);
module_exit(module_end);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
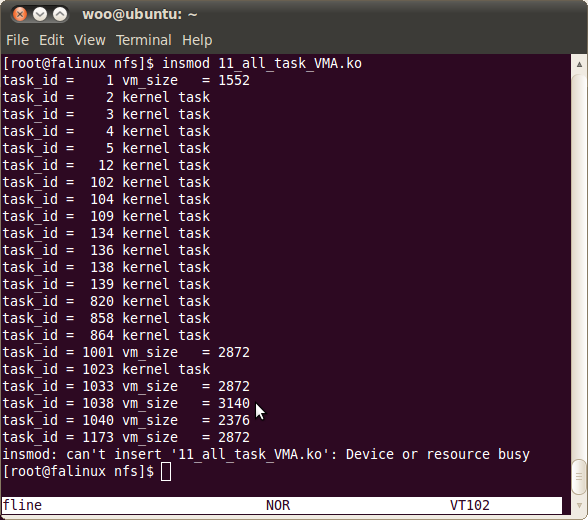
출력한 모습은 다음과 같습니다.
이로써 프로세스의 메모리영역을 출력 해보았습니다.
오늘은 여기까지 하겠습니다~ ㅎㅎ
그럼 다음시간에 만나요~~