
그래픽 & 멀티미디어
gx 라이브러리에 이번에는 원 그리기를 추가했습니다. 실은 원 그리기 함수를 넣지 않으려고 했습니다. 타원 그리기로도 원을 그릴 수 있기 때문이죠. 그러나 임베디드 보드가 조금 느리다라는 생각과 여기 강좌란에서 완벽한 그래픽 라이브러리를 만든다는 것 보다는 교육을 위한 필요도 있어서 추가하기로 했습니다.
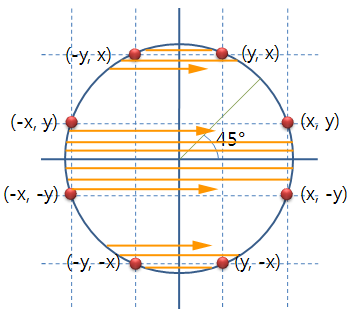 역시 Device Context의 pen_color와 brush_color을 사용하여 테두리와 내부를 채웁니다. 한번의 원 그리기 루틴으로 내부의 선을 긋고 테두리에 점을 찍으면 빠르겠습니다만, 칼라 처리와 원의 테두리를 적용한다든지의 업그레이드를 위해 2번에 나누어 처리하겠습니다.
역시 Device Context의 pen_color와 brush_color을 사용하여 테두리와 내부를 채웁니다. 한번의 원 그리기 루틴으로 내부의 선을 긋고 테두리에 점을 찍으면 빠르겠습니다만, 칼라 처리와 원의 테두리를 적용한다든지의 업그레이드를 위해 2번에 나누어 처리하겠습니다.
한번은 내부의 선을 긋고, 2번째 호출로 테두리 점을 찍습니다.
gx_circle()
| |||||||||
|
gx_circle()은 gx_rectangle와 마찬가지로 dc의 pen_color로 테두리를 그리고 brush_color로 내부 색을 채웁니다. 또한 pen_color 나 brush_color 가 clr_clear 일 경우 칠해지지 않습니다.
gx_circle()은 원을 그리는 함수 circle()을 호출하면서 내부의 색을 칠해주는 함수의 포인터와 외부의 테두리에 점을 찍은 함수의 포인터를 넘겨 줌으로써 하나의 원 그리기 루틴으로 두가지 작업을 처리합니다.
void gx_circle( dc_t *dc, int center_x, int center_y, int radius)
{
if ( 0 == radius) return;
if ( clr_clear != dc->brush_color) circle( dc, center_x, center_y, radius, dc->brush_color, dc->hline);
if ( clr_clear != dc->pen_color ) circle( dc, center_x, center_y, radius, dc->pen_color , circle_dot);
}
gx_circle()에서 색상에 따라 두번의 호출을 하면서 선을 그리는 hline()과 circle_dot() 함수를 넘겨 줍니다.
static void circle( dc_t *dc, int center_x, int center_y, int radius, int color,
void (*fun)( dc_t *dc, int, int, int, int))
{
int coor_x;
int coor_y;
int p_value;
coor_x = 0;
coor_y = radius;
p_value = 3 - 2 * radius;
while ( coor_x < coor_y)
{
draw_circle( dc, center_x, center_y, coor_x, coor_y, color, fun); // 1/8의 원 출력
if ( p_value < 0)
{
p_value += 4 * coor_x +6;
}
else
{
p_value += 4 * ( coor_x -coor_y) +10;
coor_y--;
}
coor_x++;
}
if ( coor_x == coor_y)
draw_circle( dc, center_x, center_y, coor_x, coor_y, color, fun); // 1/8의 원 출력
}
원의 1/8 부분을 대칭으로 8개의 부분을 모두 그리는 루틴입니다.
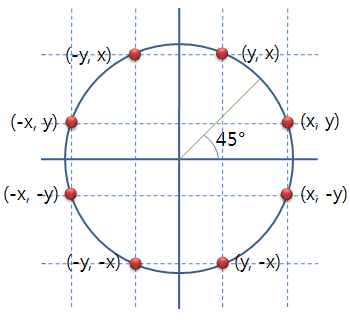
static void draw_circle( dc_t *dc, int center_x, int center_y,
int coor_x, int coor_y, int color,
void (*fun)( dc_t *c, int, int, int, int))
{
int y_dot;
y_dot = center_y +coor_y;
fun( dc, center_x-coor_x, center_x+coor_x, y_dot, color);
y_dot = center_y -coor_y;
fun( dc, center_x-coor_x, center_x+coor_x, y_dot, color);
y_dot = center_y +coor_x;
fun( dc, center_x-coor_y, center_x+coor_y, y_dot, color);
y_dot = center_y -coor_x;
fun( dc, center_x-coor_y, center_x+coor_y, y_dot, color);
}
이 함수에서 실제로 원을 그리는 함수는 fun() 입니다. 이 함수에 따라서 점의 테두리를 위한 점을 찍을 수 있으며, 또는 원의 내부를 칠할 수 있습니다.
원의 테두리 점을 찍는 함수는 인수로 받은 좌표를 좌우로 해서 점을 출력하게 됩니다.
static void circle_dot( dc_t *dc, int fst_x , int snd_x , int coor_y, int color)
{
dc->set_pixel( dc, fst_x, coor_y, color);
dc->set_pixel( dc, snd_x, coor_y, color);
}
sample 소스 설명
int rand_color( dc_t *dc) // 색상을 랜덤하게 구한다.
{
return ( gx_color( dc, rand() %128 +128, rand() %128 +128, rand() %128 +128));
}
void test_rectangle( dc_t *dc)
{
int coor_x, coor_y;
int radius;
static int ndx = 0;
coor_x = rand() % dc->width; // 원의 좌표를 랜덤으로 구합니다.
coor_y = rand() % dc->height;
radius = rand() % 100;
if ( !( ndx % 60)) gx_clear( dc, clr_black); // 매 호출 60번째 마다
// 검정색으로 Clear
switch ( (ndx++ / 20) % 3) // 매번 20번째 마다
{ // 테두리와 브러쉬 색상 처리를 바꿈
case 0 :
dc->pen_color = rand_color( dc);
dc->brush_color = clr_clear;
break;
case 1 :
dc->pen_color = clr_clear;
dc->brush_color = rand_color( dc);
break;
default :
dc->pen_color = rand_color( dc);
dc->brush_color = rand_color( dc);
break;
}
gx_circle( dc, coor_x, coor_y, radius);
usleep( 150 *1000);
}
void test( void)
{
화면에 대한 Device Context를 구하고 성공하면 test_circle() 호출
}
int main( void)
{
gx 라이브러리를 초기화하고 성공하면 test() 호출
}
프로그램을 실행하면 아래와 같이 계속 원을 출력하게 됩니다.

태그: *그래픽 *라이브러리 *그래픽라이브러리


